MBeran OPEC
High School / History / Middle Eastern History
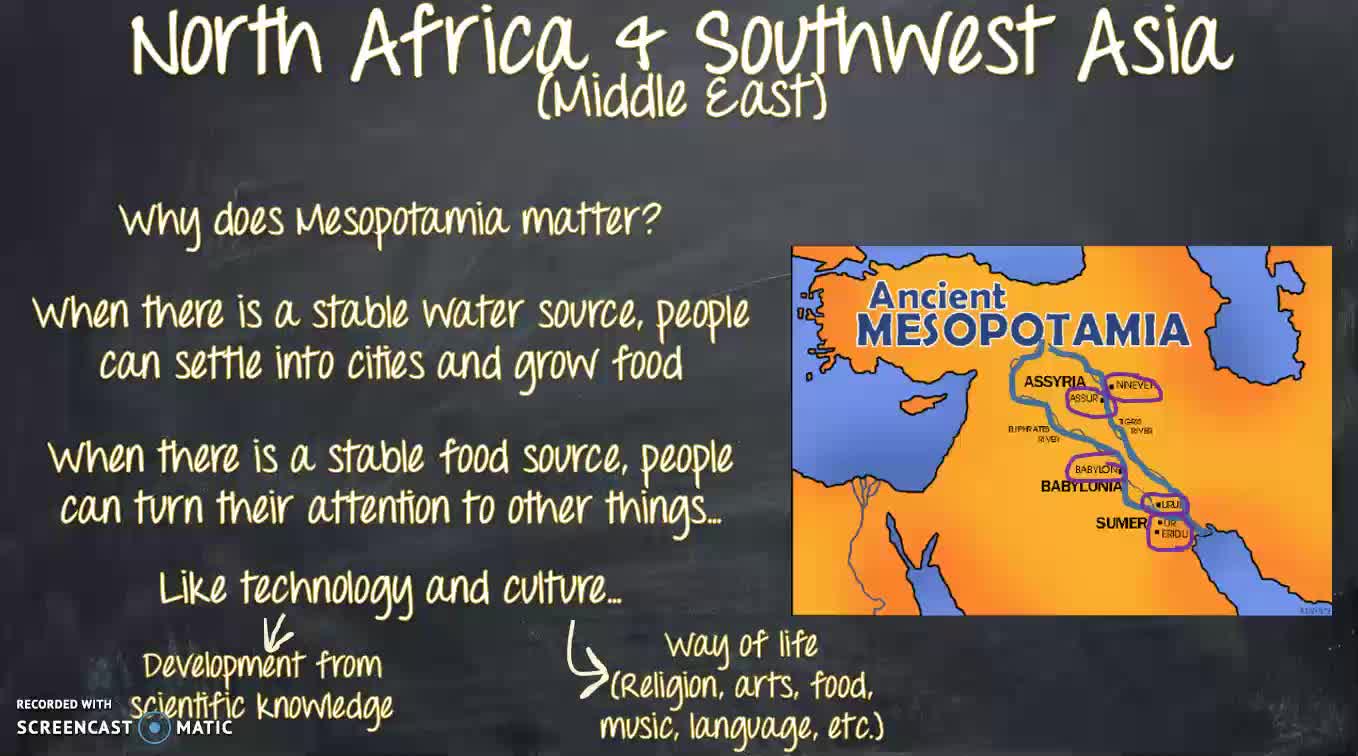
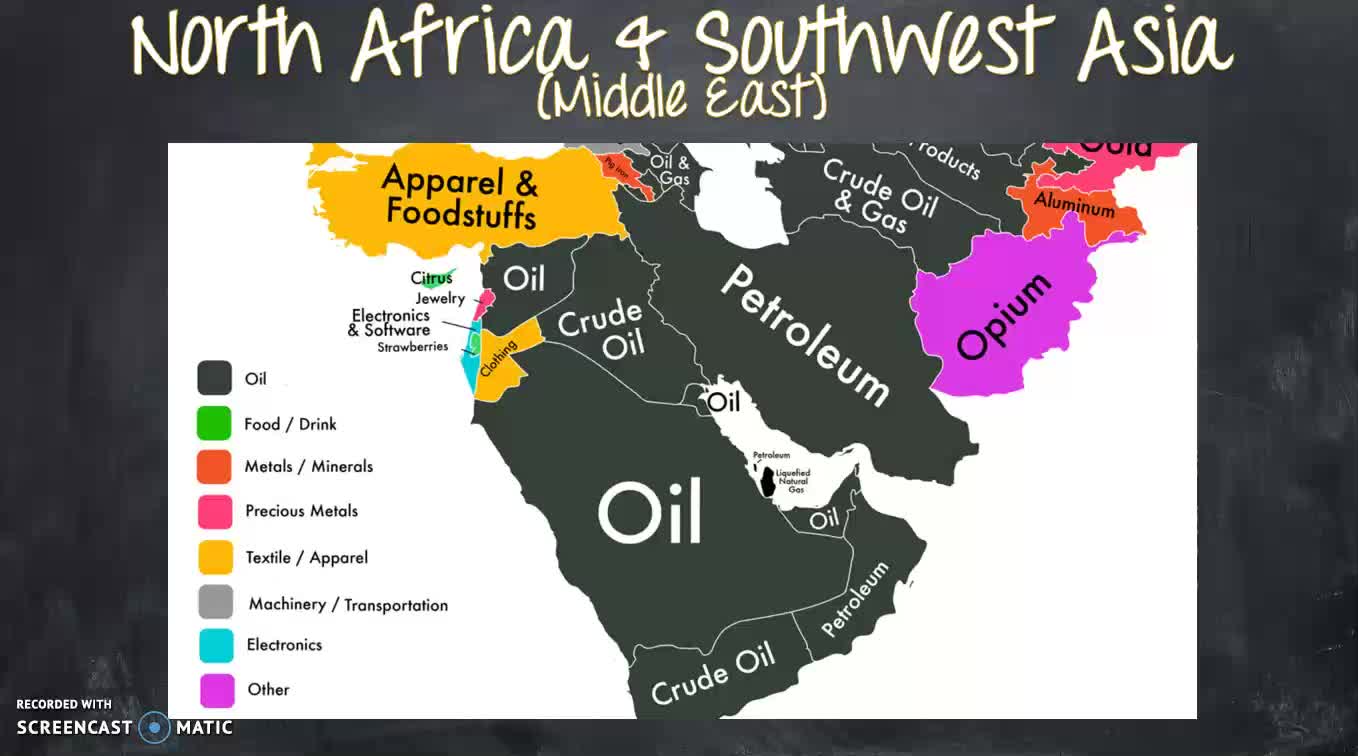
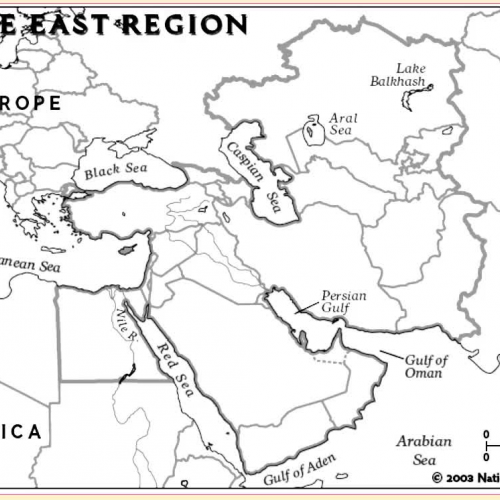
Here we go in North Africa and Southwest Asia also commonly called the Middle East, so remember when we're looking at the map, we've got Africa and Asia and the Middle East is the area kind of in the middle between Africa and Asia. And remember when we're talking about climate, the we're talking about the typical average weather over a long period of time. A desert is a dry barren land that is without water or vegetation. And air it means that a place is dry or having little or no rain. So we can tell on this map that this Middle East area is very arid. We know arid is drier having little or no rain. Which means it's going to be a really difficult place to live, right because this area is very arid, it's made up of a lot of desert, so why do people live there? Let's look at this resources map of the area. This country's main export is oil and this country's main export is oil and petroleum oil, oil, oil, oil, oil. That's why people live there. I notice that all of these countries have major export industries in oil, and oil is a very profitable business to be in that means profitable means you can make a lot of money. So people live there. People work there. It's not uncommon, especially here in the Houston area, where we know a lot of people work in the oil industry in Houston. Her people to travel over to the Middle East and work there for people to actually go live for several years over in the Middle East and work for an oil company there. So if that's something that sounds awesome to you, like you want to go live in a different place and experience different culture. Learn Arabic and that'll put you learn Arabic and go to school for petroleum industry of some kind of petroleum industry degree, oil industry degree, and you will be on our way to experiencing a completely different part of the world. So let's take a look at these maps, right? Again, you can tell on this map. It says the oil corridor, and that all those brown spots. Our oil or gas fields, so clearly they are all over the Middle East, especially a lot in Iran. I am same here, this is our oil production map, and in the key in the upper right hand tells us that each one of those bare barrels stands for a million barrels per day. So when I look at Egypt, 1 million barrel per day, when I look at Saudi Arabia, one, two, three, four, 5, 6, 7 and a half, 7 and a half million barrels per day. That's a lot of oil. So let's talk about what oil is used for. So it tells us fuels and petrochemicals. Transportation fuels are essential to the mobility of people, goods, and services, and our quality of life. Some refined products are used directly as transportation, fuels, while others are sent to patch a chemical plants where they are turned into thousands of essential products we use in our everyday lives. Right? I mean, we're from Pasadena, we're from Houston, we're from deer park. We get petrochemical plants, right? We see those all the time once 25. What a lot of the plants are doing is taking that oil and turning it into a cosmetics. Textiles and plastics, all growing up, my dad worked for a company that took oil and changed it in the plastics. So oil is used for a lot of things that you don't necessarily realize that it's used for. You're probably touching about ten different products right now that are made out of oil, whether it's a makeup that you've put on your face, the soap or shampoo that you hopefully have used, today or in the past couple days, if you haven't, you know, start using soap. The clothes that you're wearing, the backpack that you carry, the plastic on the computer keyboard that you're using, all of these things are made out of oil. So you can see how it's a really important resource, not to mention, if oil is not going to a chemical plant, it's going to go through fuel distribution, may be made into gas diesel jet fuel. All of these options that help not only people get where they need to be, but help other products to get where they need to be, right? And shipping containers going across the ocean, shipping containers going across the United States on trains and things like that. So oil is a huge resource that we use a lot of and that countries all over the world use a lot of. So that gives them the Middle East and a huge influence over the rest of the world be his they have access to a lot of this oil, a lot of this resource that just about everybody else needs to live, what we would consider a modern developed life. So, to protect that and to help with oil production and oil prices, there is a group that was caught formed called OPEC. An OPEC stands for the organization of petroleum exporting countries, petroleum is a word that we use, fairly interchangeably with oil. And exporting means countries that send it out to other places that sell it to other places. So they're not keeping it in their country. I mean, if even some of it obviously, but they're selling a lot of it to other countries that don't have big oil resources and big oil reserves. So OPEC is the organization of petroleum exporting countries. It was founded in 1960. And it currently has 13 member countries. Okay, here they are. And you'll notice most of them are in the Middle East or Africa, but not all of them. We've got a couple of countries over in South America Venezuela and Ecuador. But just about all the other countries are either in what's considered the Middle East or in just an Africa. But all of these countries work together and their goal is to protect oil resources, and keep the profit, profits, for the countries that own them. Okay, so instead of letting foreign countries come in and control all their oil, they are going to control their own oil resources. They're going to keep all the profits or the money made for themselves, right? That's kind of smart business thing. So OPEC is what you call a cartel. I know my students may be familiar with the term cartel in other ways, but we are talking about a cartel in a legitimate business fashion, and in a cartel is an organization that works together to support high prices for a particular resource. Okay, so what does that mean? Well, before OPEC, before this cartel, Saudi Arabia might sell its oil for $2 a barrel. So I ran my sell it for a dollar 90. So I don't remember what country this was. Oh, Venezuela, that's what it was. So I'm Venezuela, might sell it for a dollar 85. And then Nigeria might sell it for 80. So because these countries are competing against one another, and they want to get the most business. They're having to just lower their prices a little bit in a little bit. Under the under the guy before him, so that people will come by theirs because if Nigeria is selling their oil for a dollar 80 and Saudi Arabia is selling their oil for $2 a barrel, then you're going to go with Nigeria, right? So these guys are competing, and so then Saudi Arabia is going to have to lower their prices. Okay, so that's kind of how it all works. And so basically everybody's just fighting for customers, right? So everybody's fighting for customers everybody's lowering their prices. It's not really working out and the best for anybody because if you're having to lower your prices, you're not making as much money. But with OPEC, it's a cartel, or an organization that works together to support high prices, not lowering prices. They want to raise prices. So Saudi Arabia is going to sell their oil for $10 a barrel, and then Iran is going to sell theirs for $10 a barrel, and Venezuelans can sell theirs for $10 a barrel and Nigeria's can sell their $10 a barrel. So because they're no longer competing, because they're all working together. They can just say, hey, let's also our oil for $10 a barrel instead of lowering our prices to $2 and one 50, and then no matter who the oil is bought from, we're all going to make more money. Okay? So how does that work realistically? Well, in oil in 1960, was less than $2 a barrel. Oil today is around $70 a barrel. That's a significant increase. That's a $68 increase in the price of oil and now inflation in all other kinds of things go into that. But OPEC has certainly helped these countries raise their prices because they're not having to compete with one another to have lower prices. So OPEC is the organization of petroleum, exporting countries, right when you're petroleum is oil, exporting means sending it out, selling it out, so they are selling their oil. These are countries that are selling oil out to other countries of the world, because every country doesn't have oil resources. We know we have a lot in Texas. We have in the United States. Significant oil resources in Mexico has some Canada also has huge resources we learned in our last unit that Russia has huge oil resources. So every country that has oil is not a member of OPEC, but quite a few of them are, quite a few of the world's biggest oil producing countries are, and that's just helps the OPEC countries stabilize the prices and keep prices high so they can make it makes we can make as much money as possible, right? So OPEC is the organization of petroleum exporting countries. It was founded in 1960. There are 13 current member countries right here they are we know that they're mostly in the Middle East and Africa but also a couple in South America you'll notice over in the left underneath the OPEC logo that United States Canada, Mexico or not part of OPEC. But they still affect our lives because of how much oil they control in the world. And the goal is to protect oil resources and keep the profits for the countries that own them, right? So let's go back to this map. Iran wants to protect its oil resources. And because Iran wants to make the money from that oil, they don't want to let someone else get all the money from their oil. Same with you'll see Saudi Arabia, Qatar. Wait, all of these countries are using OPEC to help charge higher prices, and help keep all the money all the profits in their country to develop their own countries, instead of letting other countries or foreign corporations come in and take advantage of the resources that they have. So that is OPEC. Thanks for watching.